Mixed-Integer linear programming
| Class date(s): | 25 March 2015 | ||||
| |||||
| |||||
| |||||
| |||||
Resources
Scroll down, if necessary, to see the resources.
| Date | Class number | Topic | Slides/handouts for class | Video file | References and Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 March | 11B |
|
Video |
See the GAMS codes below | |
| 30 March | 12A |
More problems that can be solved with integer variables
|
Video |
See the GAMS codes below | |
| 01 April | 12B |
The branch and bound procedure to solve integer problems |
Video |
See code below to solve the original problem, and then the relaxed problem. See another example problem below (with solution). | |
| 06 April | 13A |
Working towards understanding schedule problems in engineering
|
Video |
See code below to simple scheduling problem. | |
| 08 April | 13B |
More problems that can be solved with integer variables:
|
|
Solving a basic ILP
free variable income "total income";
positive variables x1, x2;
binary variable delta "use ingredient x3 or not at all";
EQUATIONS
obj "maximize income",
blend "blending constraint";
obj.. income =E= 18*x1 - 3*x2 - 9*(20*delta);
blend.. 2*x1 + x2 + 7*(20*delta) =L= 150;
x1.up = 25;
x2.up = 30;
model recipe /all/;
SOLVE recipe using MIP maximizing income;
Solving the knapsack problem
free variable value "total value";
sets j "item j" /1*5/;
binary variables x(j) "whether to include item in the knapsack";
parameter v(j) "value of object j"
/1 4,
2 2,
3 10,
4 1,
5 2/;
parameter w(j) "weight of object j"
/1 12,
2 1,
3 4,
4 1,
5 2/;
EQUATIONS
obj "maximize value",
weight "weight constraint";
obj.. value =e= sum(j, v(j)*x(j));
weight.. sum(j, w(j)*x(j)) =L= 15;
model knapsack /all/;
solve knapsack using mip maximizing value;
Solving the knapsack problem for selecting amount projects, with constraints
free variable value "total value";
sets j "item j" /1*5/;
binary variables x(j) "whether to include item in the project";
parameter v(j) "value of object j"
/1 50,
2 72,
3 25,
4 41,
5 17/;
parameter w(j) "cost of object j"
/1 8,
2 21,
3 15,
4 10,
5 7/;
EQUATIONS
obj "maximize value",
weight "weight constraint",
me1v2 "1 and 2 are mutually exclusive",
me1v3v5 "1, 3 and 5 are mutually exclusive",
d4v3 "4 depends on 3";
obj.. value =e= sum(j, v(j)*x(j));
weight.. sum(j, w(j)*x(j)) =L= 35;
me1v2.. x('1') + x('2') =L= 1;
me1v3v5.. x('1') + x('3') + x('5') =L= 1;
d4v3.. x('4') =L= x('3');
model projects /all/;
solve projects using mip maximizing value;
Binary problem relaxation
This is the problem we looked at in class for the generators.
Notice that the only differences are:
- the binary variables become positive variables, thepr
- the problem is solved as an LP not an MIP
- the constraints for .LO and .UP are added, where required, depending on the partial solution solved
| Original problem solved in class | Relaxed problem solved in class |
|---|---|
free variable cost "total cost";
sets j "item j" /1*4/;
binary variables x(j) "whether to use generator";
parameter c(j) "cost of using generator j"
/1 7,
2 12,
3 5,
4 14/;
parameter p(j) "power of generator j"
/1 300,
2 600,
3 500,
4 1600/;
EQUATIONS
obj "cost",
power_constraint;
obj.. cost =e= sum(j, c(j)*x(j));
power_constraint.. sum(j, p(j)*x(j)) =G= 700;
MODEL purchase /all/;
SOLVE purchase using MIP minimizing cost;
|
free variable cost "total cost";
sets j "item j" /1*4/;
positive variables x(j) "whether to use generator";
parameter c(j) "cost of using generator j"
/1 7,
2 12,
3 5,
4 14/;
parameter p(j) "power of generator j"
/1 300,
2 600,
3 500,
4 1600/;
EQUATIONS
obj "cost",
power_constraint;
obj.. cost =e= sum(j, c(j)*x(j));
power_constraint.. sum(j, p(j)*x(j)) =G= 700;
* Solve the problem for the partial solution: (#, 0, #, 1)
x.LO('1')=0;
x.UP('1')=1;
x.LO('2')=0;
x.UP('2')=0;
x.LO('3')=0;
x.UP('3')=1;
x.LO('4')=1;
x.UP('4')=1;
MODEL purchase /all/;
SOLVE purchase using LP minimizing cost;
|
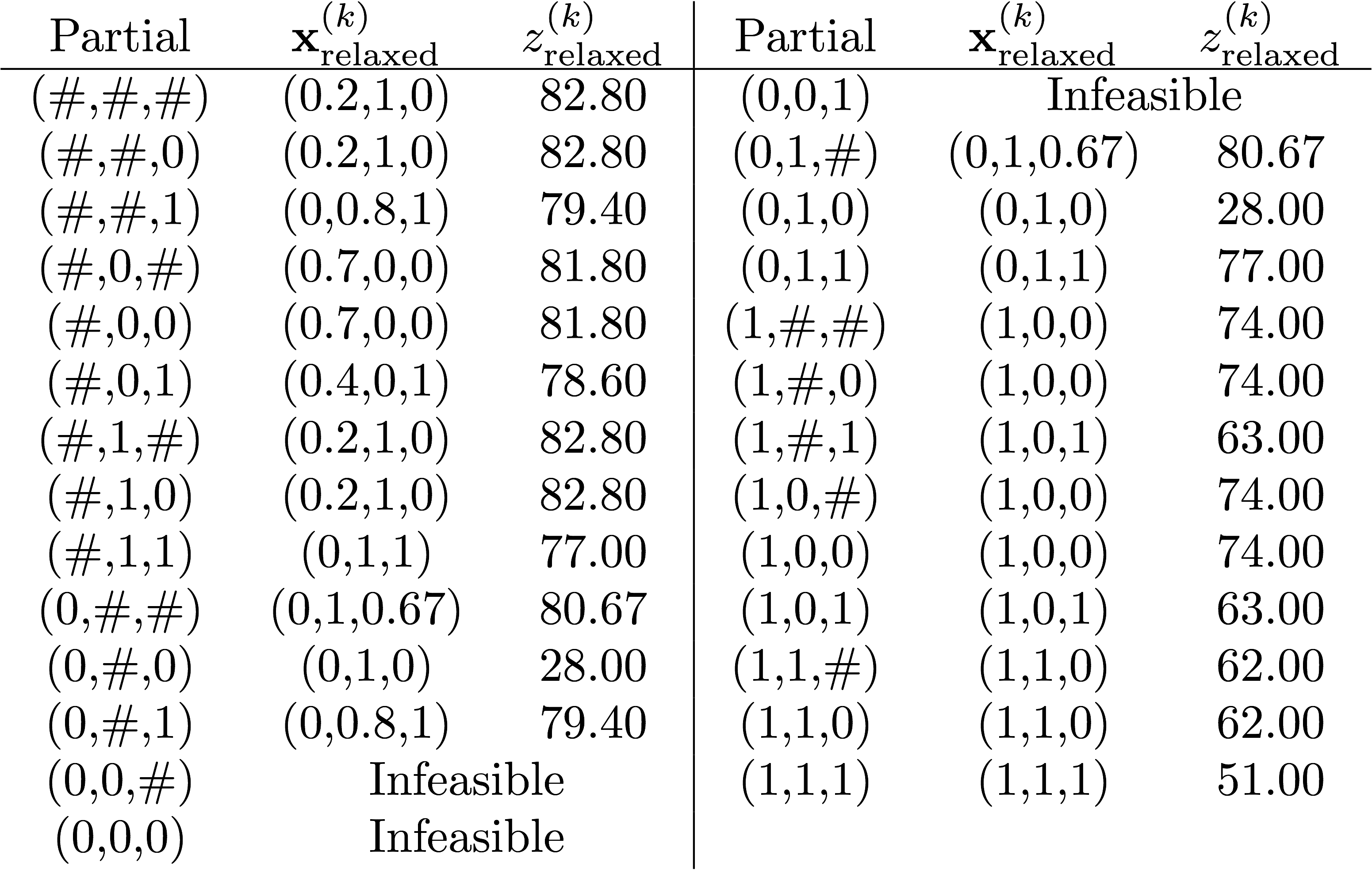
Example problem to practice
The objective is to maximize the objective function value, \(z\). The table or partial solutions is provided below. The only constraints are that all the 3 search variables must be binary (0 or 1). The "relaxed" refers to the relaxed problem solution.
Use the depth-first search method, and when branching, choose the branch with \(x_i = 0\) before the \(x_i=1\) branch.
If you do this, your nodes will have the following solution order:
Node 0 \((z=82.80)\)
Node 1 \((z=80.67)\)
Node 2 \((z=28.00)\) [incumbent]
Node 3 \((z=79.4)\)
Node 4 \((z=\text{Infeasible})\)
Node 5 \((z=77.00)\) [incumbent; turns out this is the eventual optimum]
Node 6 \((z=74.00)\)
[The end: can you prove why?]