Difference between revisions of "Assignment 8 - 2012"
Kevin Dunn (talk | contribs) (Created page with "== Troubleshooting tutorial == The troubleshooting tutorial ("The Triads") is a concept developed by Don Woods at McMaster University. Each person in the class will perform 3...") |
Kevin Dunn (talk | contribs) |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Troubleshooting tutorial == | == Troubleshooting tutorial == | ||
The troubleshooting tutorial ("The Triads") is a concept developed by Don Woods at McMaster University. Each person in the class will perform 3 troubleshooting exercises, rotating your role in each exercise (about 30 minutes per exercise). | The troubleshooting tutorial ("The Triads") is a concept developed by Don Woods at McMaster University. Each person in the class will perform 3 troubleshooting exercises, rotating your role in each exercise (about 30 minutes per exercise). There is more information on troubleshooting in [[Course_pack_for_2012 | tab 6 of your course pack]]. | ||
[[Image:Triad-Troubleshooting.jpg|800px]]''click for larger version'' | [[Image:Triad-Troubleshooting.jpg|800px]]''click for larger version'' | ||
| Line 22: | Line 20: | ||
You will have received a binder before the tutorial, read over this background material. Understand the process extremely well. Think about how "the fault" will affect all of the process variables. Try to anticipate the kinds of questions that the Troubleshooter might ask; or experiments that he/she might ask to be performed. What would the fault do to the system under those conditions? Give results of experiments. '''Do not give explanations'''. Give correct information but do not be generous. If, for example, the fault occurs periodically, and you are asked to give the lab analysis for one sample taken: assume Murphy's law applies and give them the result when the system was operating normally. | You will have received a binder before the tutorial, read over this background material. Understand the process extremely well. Think about how "the fault" will affect all of the process variables. Try to anticipate the kinds of questions that the Troubleshooter might ask; or experiments that he/she might ask to be performed. What would the fault do to the system under those conditions? Give results of experiments. '''Do not give explanations'''. Give correct information but do not be generous. If, for example, the fault occurs periodically, and you are asked to give the lab analysis for one sample taken: assume Murphy's law applies and give them the result when the system was operating normally. | ||
Insist that they write out all requests; write down the results | Insist that they write out all requests; write down the results. Do not talk..... just acknowledge that they are working on it by saying "Ahemmm, mmmmm," | ||
Insist on their instructions, or requests be written precisely. | Insist on their instructions, or requests be written precisely. | ||
Latest revision as of 00:19, 15 November 2012
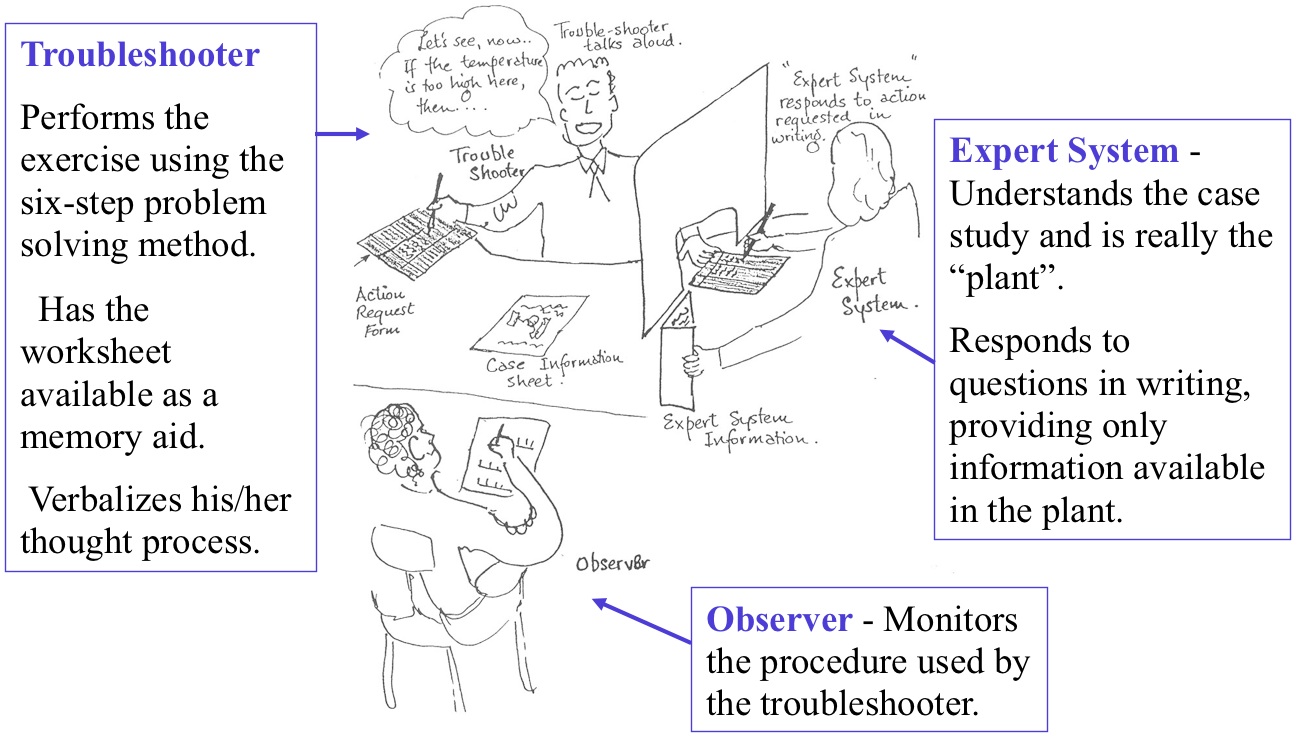
Troubleshooting tutorial
The troubleshooting tutorial ("The Triads") is a concept developed by Don Woods at McMaster University. Each person in the class will perform 3 troubleshooting exercises, rotating your role in each exercise (about 30 minutes per exercise). There is more information on troubleshooting in tab 6 of your course pack.
Observer
As the Troubleshooter is tackling the problem, your task is to assess how well the problem solving components are handled. This is challenging because the skills are difficult to identify let alone observe and assess. The evaluation sheet is made to help you look at the mental process used by the trouble shooter. Try to focus more on the "types of questions asked", and " how can I create a hypothesis and test it?" and not on "what information do I need?" or on "what action should I take?". Look at the organizational pattern used; listen for the monitoring of the process. Consider, "does he/she confuse activities unknowingly?"
Let the Expert System focus on "how well the trouble shooter wrote out the questions and tasks to be done".
You will provide feedback on the troubleshooter's performance after the exercise.
Expert System
You will have received a binder before the tutorial, read over this background material. Understand the process extremely well. Think about how "the fault" will affect all of the process variables. Try to anticipate the kinds of questions that the Troubleshooter might ask; or experiments that he/she might ask to be performed. What would the fault do to the system under those conditions? Give results of experiments. Do not give explanations. Give correct information but do not be generous. If, for example, the fault occurs periodically, and you are asked to give the lab analysis for one sample taken: assume Murphy's law applies and give them the result when the system was operating normally.
Insist that they write out all requests; write down the results. Do not talk..... just acknowledge that they are working on it by saying "Ahemmm, mmmmm,"
Insist on their instructions, or requests be written precisely.
If they write, " Inspect the instrument" then respond "It's OK". If they ask what you did, then say "I went out and looked at it." Be tough. Do not offer more information than they asked for.
You will discuss the solution with your two colleagues after the exercise.
- Please do not share information about your case with anyone.
- Do not mark the stapled sheets in the folder; these folders are reused in future years and cost substantial time and money to prepare.
Troubleshooter
You have a challenging role to play.
You are to talk aloud so that the Observer can track what you are doing. Think about the process you will be using: are you searching for change or for hypotheses; whether you are clarifying the situation or testing an idea. You may feel frustrated because the Expert System is going to supply written responses to your requests; the Expert System will not discuss things with you. He/she may say "Hmmm" or "mmmmmm" to you occasionally so that you do not feel too much like talking to a wall but basically the Expert System is there to provide instant system written response to your requests.
You are to display all the good problem solving skills we have developed. Do this by verbally monitoring your progress, being active with pencil and paper to keep track of the route you are following,
You are to write out your requests for information from the Expert System. These should be written out precisely. A sample form is given below.