Difference between revisions of "Principal Component Analysis"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Kevin Dunn (talk | contribs) m (→Class 3) |
Kevin Dunn (talk | contribs) |
||
| (11 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | {{ClassSidebarYouTube | ||
== Class 2 | | date = 16, 23, 30 September 2011 | ||
| vimeoID1 = 9QzNOz_7i6U | |||
| vimeoID2 = qDiPZp-FWc4 | |||
| vimeoID3 = y0Alf0VZ-1E | |||
| vimeoID4 = XfH_p1WAydM | |||
| vimeoID5 = QLB-UJ1dFiE | |||
| vimeoID6 = bysqF41Mgc0 | |||
| vimeoID7 = p3i-XsviARM | |||
| vimeoID8 = Qb28yc3eM0Q | |||
| vimeoID9 = | |||
| course_notes_PDF = | |||
| course_notes_alt = Course notes | |||
| overheads_PDF = | |||
| overheads_PDF_alt = Projector notes | |||
| assignment_instructions = | |||
| assignment_solutions = | |||
| video_download_link_MP4 = http://learnche.mcmaster.ca/media/LVM-2011-Class-02A.mp4 | |||
| video_download_link2_MP4 = http://learnche.mcmaster.ca/media/LVM-2011-Class-02B.mp4 | |||
| video_download_link3_MP4 = http://learnche.mcmaster.ca/media/LVM-2011-Class-02C.mp4 | |||
| video_download_link4_MP4 = http://learnche.mcmaster.ca/media/LVM-2011-Class-03A.mp4 | |||
| video_download_link5_MP4 = http://learnche.mcmaster.ca/media/LVM-2011-Class-03B.mp4 | |||
| video_download_link6_MP4 = http://learnche.mcmaster.ca/media/LVM-2011-Class-03C.mp4 | |||
| video_download_link7_MP4 = http://learnche.mcmaster.ca/media/LVM-2011-Class-04A.mp4 | |||
| video_download_link8_MP4 = http://learnche.mcmaster.ca/media/LVM-2011-Class-04B.mp4 | |||
| video_download_link9_MP4 = | |||
| video_download_link_MP4_size = 290 Mb | |||
| video_download_link2_MP4_size = 306 Mb | |||
| video_download_link3_MP4_size = 294 Mb | |||
| video_download_link4_MP4_size = 152 Mb | |||
| video_download_link5_MP4_size = 276 Mb | |||
| video_download_link6_MP4_size = 333 Mb | |||
| video_download_link7_MP4_size = 198 Mb | |||
| video_download_link8_MP4_size = 180 Mb | |||
| video_download_link9_MP4_size = Mb | |||
| video_notes1 = | |||
| video_notes2 = | |||
| video_notes3 = | |||
| video_notes4 = | |||
| video_notes5 = | |||
| video_notes6 = | |||
}}__NOTOC__ | |||
== Class 2 (16 September 2011) == | |||
[[Image:Nuvola_mimetypes_pdf.png|20px|link=Media:Lvm-class-2.pdf]] [[Media:Lvm-class-2.pdf|Download the class slides]] (PDF) | |||
* Download these 3 CSV files and bring them on your computer: | * Download these 3 CSV files and bring them on your computer: | ||
** Peas dataset: http:// | ** Peas dataset: http://openmv.net/info/peas | ||
** Food texture dataset: http:// | ** Food texture dataset: http://openmv.net/info/food-texture | ||
** Food consumption dataset: http:// | ** Food consumption dataset: http://openmv.net/info/food-consumption | ||
=== Background reading === | === Background reading === | ||
| Line 23: | Line 58: | ||
** matrix multiplication | ** matrix multiplication | ||
** that matrix multiplication of a vector by a matrix is a transformation from one coordinate system to another (we will review this in class) | ** that matrix multiplication of a vector by a matrix is a transformation from one coordinate system to another (we will review this in class) | ||
** [ | ** [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linear_combination linear combinations] (read the first section of that website: we will review this in class) | ||
** the dot product of 2 vectors, and that they are related by the cosine of the angle between them (see the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dot_product geometric interpretation section]) | ** the dot product of 2 vectors, and that they are related by the cosine of the angle between them (see the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dot_product geometric interpretation section]) | ||
| Line 38: | Line 73: | ||
== Class 3 == | == Class 3 (23, 30 September 2011) == | ||
[[Image:Nuvola_mimetypes_pdf.png|20px|link=Media:Lvm-class-3.pdf]] [[Media:Lvm-class-3.pdf|Download the class slides]] (PDF) | |||
===Background reading === | ===Background reading === | ||
* | * Least squares: | ||
** what is the objective function of least squares | ** what is the objective function of least squares | ||
** how to calculate the regression coefficient | ** how to calculate the regression coefficient | ||
| Line 58: | Line 86: | ||
* Some optimization theory: | * Some optimization theory: | ||
** How an optimization problem is written with equality constraints | ** How an optimization problem is written with equality constraints | ||
** The [ | ** The [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lagrange_multiplier Lagrange multiplier principle] for solving simple, equality constrained optimization problems. | ||
===Background reading === | ===Background reading === | ||
* Reading on [http://literature.connectmv.com/item/12/cross-validatory-estimation-of-the-number-of-components-in-factor-and-principal-components-models cross validation] | * Reading on [http://literature.connectmv.com/item/12/cross-validatory-estimation-of-the-number-of-components-in-factor-and-principal-components-models cross validation] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:04, 17 September 2018
| Class date(s): | 16, 23, 30 September 2011 | ||||
| |||||
| |||||
| |||||
| |||||
| |||||
| |||||
| |||||
| |||||
Class 2 (16 September 2011)
![]() Download the class slides (PDF)
Download the class slides (PDF)
- Download these 3 CSV files and bring them on your computer:
- Peas dataset: http://openmv.net/info/peas
- Food texture dataset: http://openmv.net/info/food-texture
- Food consumption dataset: http://openmv.net/info/food-consumption
Background reading
- Reading for class 2
- Linear algebra topics you should be familiar with before class 2:
- matrix multiplication
- that matrix multiplication of a vector by a matrix is a transformation from one coordinate system to another (we will review this in class)
- linear combinations (read the first section of that website: we will review this in class)
- the dot product of 2 vectors, and that they are related by the cosine of the angle between them (see the geometric interpretation section)
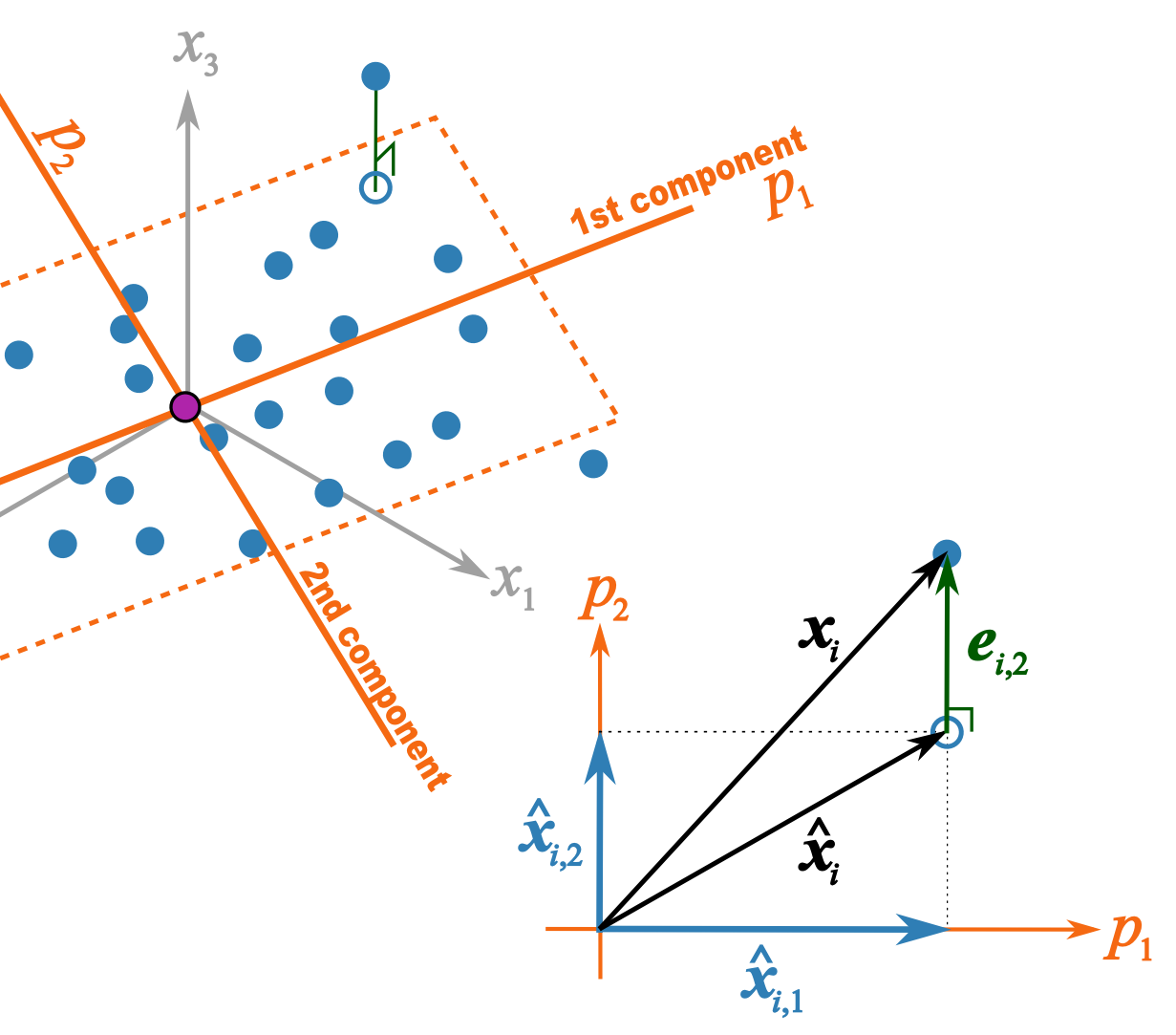
This illustration should help better explain what I trying to get across in class 2B
Class 3 (23, 30 September 2011)
![]() Download the class slides (PDF)
Download the class slides (PDF)
Background reading
- Least squares:
- what is the objective function of least squares
- how to calculate the regression coefficient
- understand that the residuals in least squares are orthogonal to
- Some optimization theory:
- How an optimization problem is written with equality constraints
- The Lagrange multiplier principle for solving simple, equality constrained optimization problems.
Background reading
- Reading on cross validation