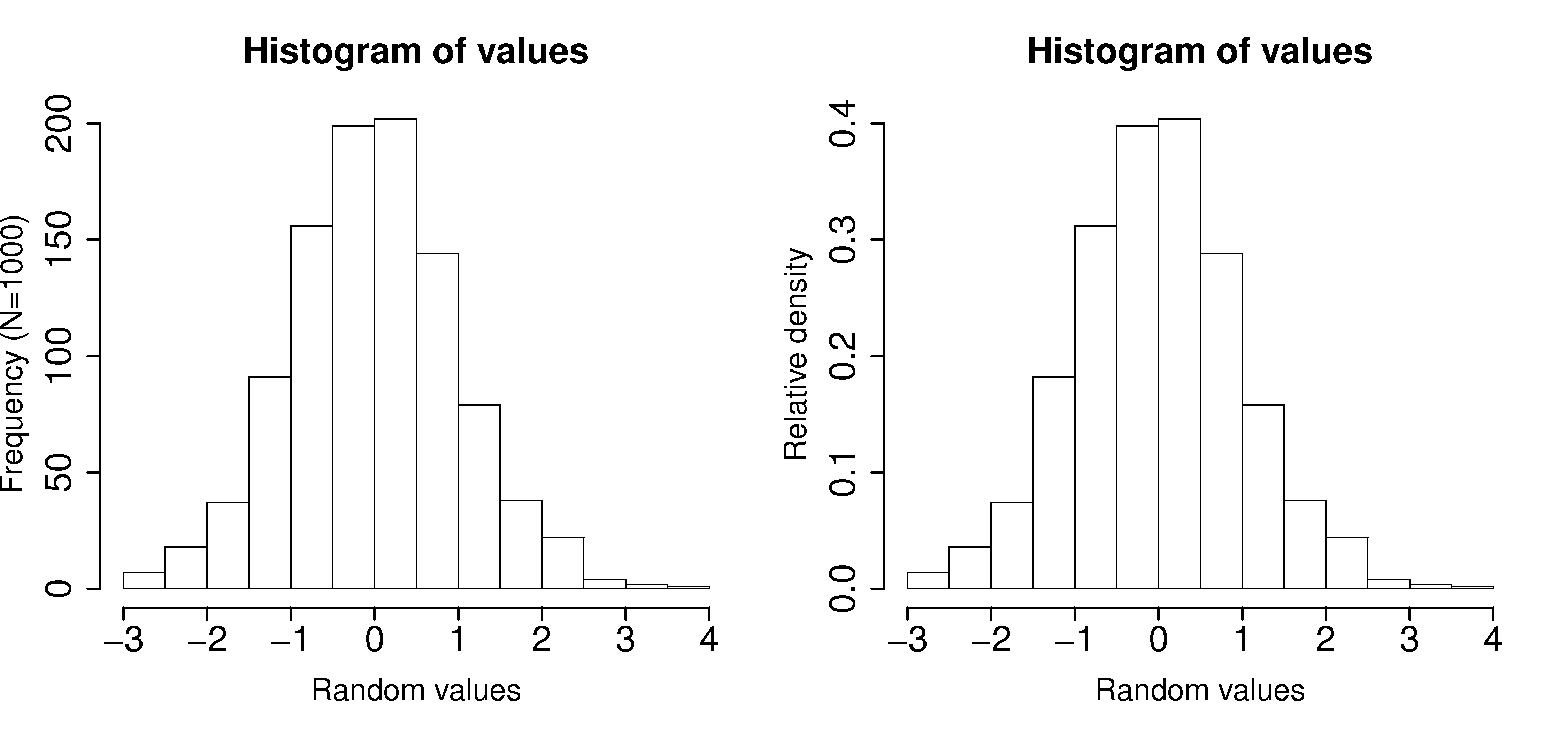2.4. Histograms and probability distributions¶
The previous section has hopefully convinced you that variation in a process is inevitable. This section aims to show how we can visualize and quantify any variability in a recorded vector of data.
A histogram is a summary of the variation in a measured variable. It shows the number of samples that occur in a category: this is called a frequency distribution. For example: number of children born, categorized against their birth gender: male or female.
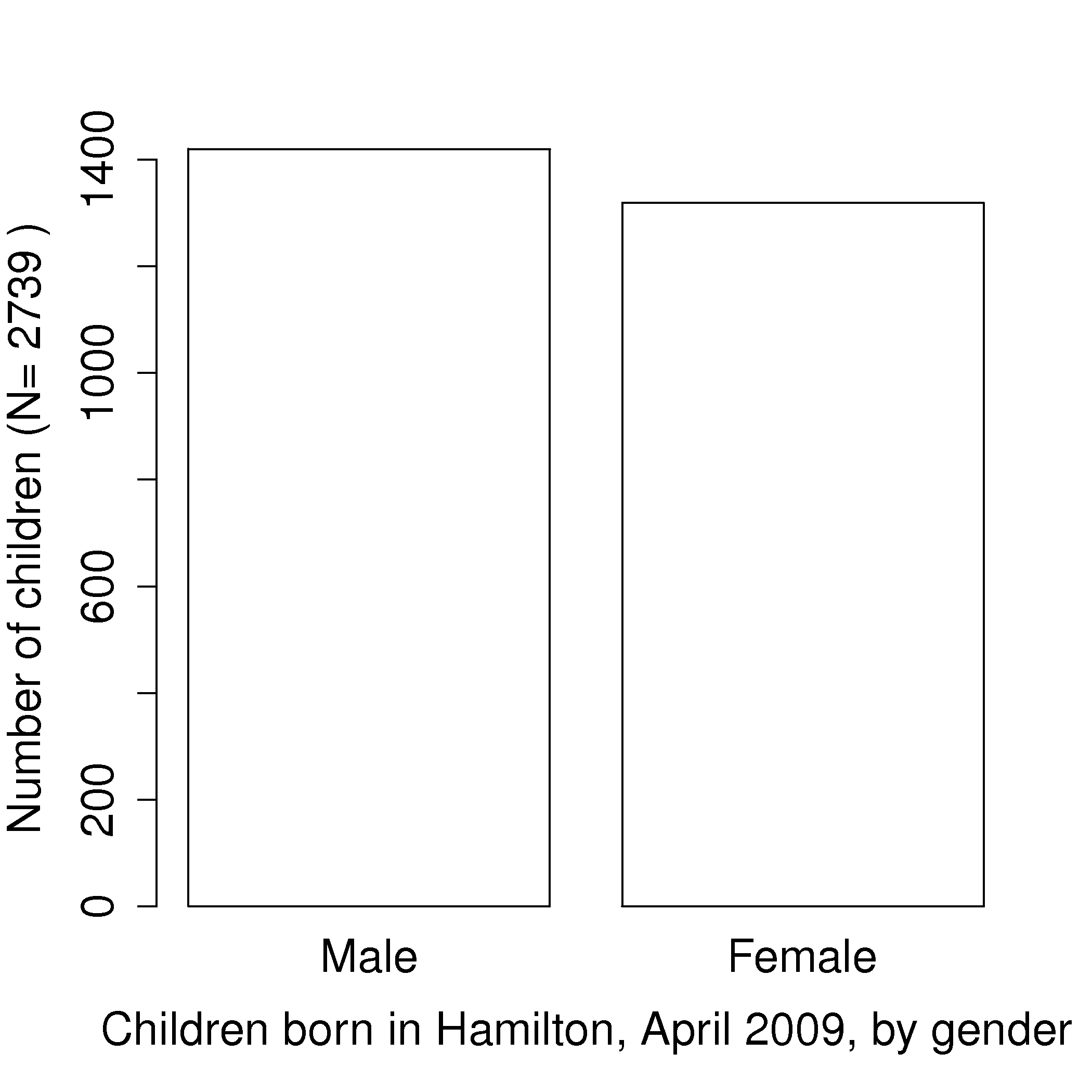
The raw data in the above example was a vector that consisted of 2739 text entries, with 1420 of them as Male and 1319 of them as Female. In this case Female and Male represent the two categories.
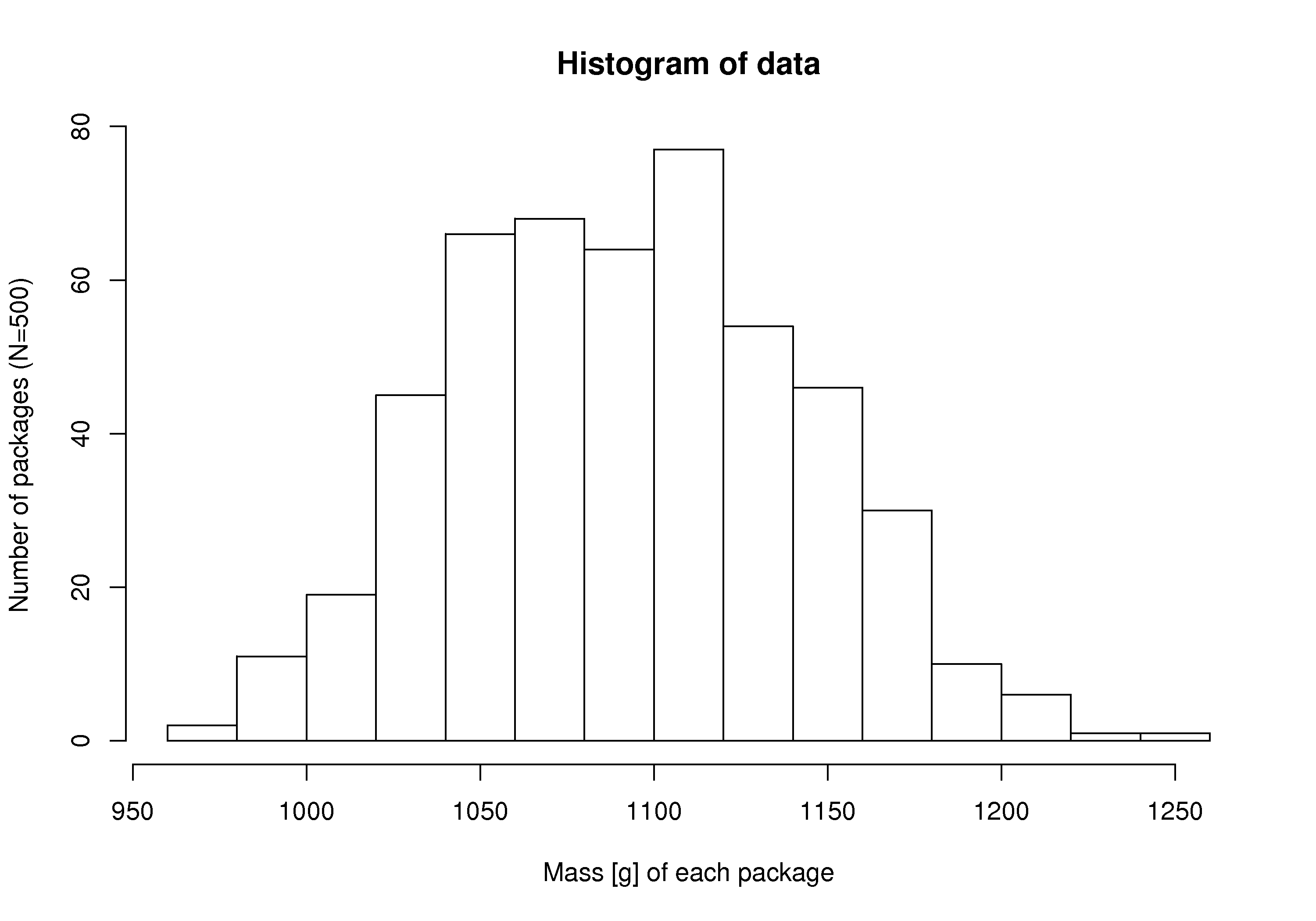
Histograms make sense for categorical variables, but a histogram can also be derived from a continuous variable. Here is an example showing the mass of cartons of 1 kg of flour. The continuous variable, mass, is divided into equal-size bins that cover the range of the available data. Notice how the packaging system has to overfill each carton so that the vast majority of packages weigh over 1 kg (what is the average package mass?). If the variability in the packaging system could be reduced - the spread of the data made narrower - then the histogram can be shifted to the left, thereby reducing overfill.
Try creating a fictitious histogram for each of the following situations:
The grades for a class for a really easy test.
The numbers thrown from a 6-sided die.
The annual income for people in your country.
Analytical measurements taken in a laboratory, by the same person or computerized process.
In preparing the above histograms, what have you implicitly inferred about time-scales? These histograms show the long-term distribution (probabilities) of the system being considered. This is why concepts of chance and random phenomena can be use to described systems and processes. Probabilities can be used to describe our long-term expectations. Let us contrast some long-term and short-term expectations next:
The long-term sex ratio at birth 1.06:1 (boy:girl) is expected in Canada; but a newly pregnant mother would not know the sex.
The long-term data from a process shows an 85% output yield from our batch reactor; but tomorrow it could be 59% and the day after that 86%.
We know that a fair die has a 16.67% chance of showing a 4 when thrown, but we cannot predict the value of the next throw.
Even if we have complete mechanistic knowledge of our process, the concepts from probability and statistics are useful to summarize and communicate information about past behaviour, and the expected future behaviour.
Steps to creating a frequency distribution, illustrated with 4 examples, labelled A, B, C, and D.
Decide what you are measuring:
acceptable or unacceptable metal appearance: yes/no
number of defects on a metal sheet: none, low, medium, high
yield from the batch reactor: somewhat continuous - quantized due to rounding to the closest integer
daily ambient temperature, in Kelvin: continuous values
Decide on a resolution for the measurement axis:
acceptable/unacceptable (1/0) code for the metal’s appearance
use a scale from 1 to 4 that grades the metal’s appearance
batch yield is measured in 1% increments, reported either as 78, 79, 80, 81%, etc.
temperature is measured to a 0.05 K precision, but we can report the values in bins of 5K
Report the number of observations in the sample or population that fall within each bin (resolution step):
number of metal pieces with appearance level “acceptable” and “unacceptable” are added up
number of pieces with defect level 1, 2, 3, 4 are counted
number of batches with yield inside each bin level are calculated
number of temperature values inside each bin level are computed
Plot the number of observations in category as a bar plot. If you plot the number of observations divided by the total number of observations, \(N\), then you are plotting the relative frequency.
A relative frequency, also called density, is sometimes preferred:
we do not need to report the total number of observations, \(N\)
it can be compared to other distributions
if \(N\) is large enough, then the relative frequency histogram starts to resemble the population’s distribution
the area under the histogram is equal to 1, and related to probability